How VPN works
To understand how AdGuard VPN works, you should at first understand the general principles of the VPN service.
VPN features
A VPN is a virtual private network that helps hide your location and protect your data on the Web. A VPN connects a computer or a mobile device to a VPN server and uses the IP address of this server to make it seem to an outside observer that you are in another place. This allows you to securely access various Internet resources and protect your personal data.
In that way, a VPN performs two important functions:
Maintaining anonymity
Using an Internet connection, the user leaves their digital footprint, which can then be analyzed and used by third parties. For example, one of the online stores that you have visited can save your search history and then offer you their products based on it through targeted advertising. Or the secret services, having learned your location through the IP address of your device and having determined your identity, can secretly monitor your activity on the web. In addition, web browsers and ISPs themselves can use your browsing history for their own purposes, as well as sell it to advertisers and provide it to government institutions. VPN allows you to hide your IP address and replace it with the IP address of the VPN server to which you are connected. This way you will be able to maintain your privacy and anonymously search for information on the web.
Data protection
If you connect to an unreliable or public network, the data on your device may become vulnerable to cybercriminals. Bank card details, usernames and passwords, passport data — all this data can be intercepted by online fraudsters. The VPN tunnel encrypts the information you send to and receive from the Web, making it useless in the wrong hands.
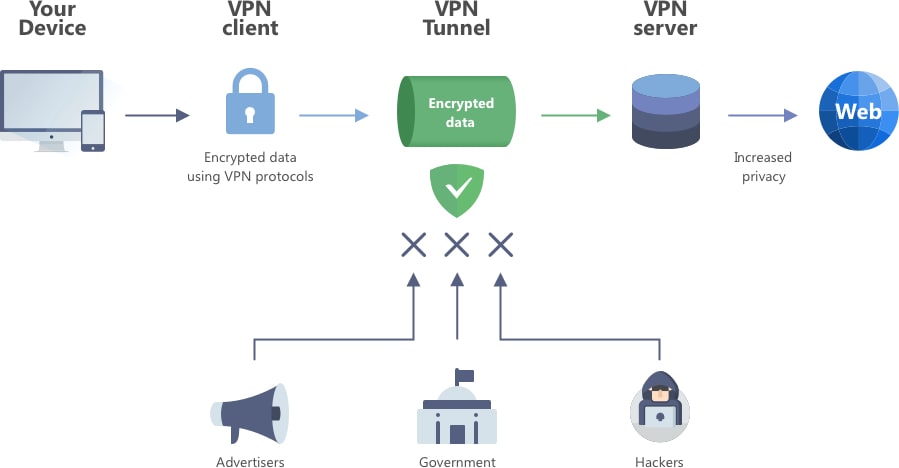
VPN structure
When you connect to a network, your computer or mobile device is assigned a unique ID number, or IP address. It usually consists of numbers from 0 to 255, separated by dots or colons. Knowing this sequence, one can determine the geolocation of the device. The IP address is usually assigned by your ISP, and it will be visible all the way to the desired resource. For this reason, the web server of the site you are visiting can register your IP address and record what you have requested. This record can then be used primarily for data collection and traffic analysis.
A VPN creates a tunnel between your device and the VPN server. Your data goes through this tunnel, gets encrypted and then enters the open Internet in a secure form. The web server therefore registers the IP address of the endpoint of the tunnel, meaning the VPN server, and thus not the device's real IP address. Thus, the site that you get to after passing through the VPN tunnel will consider the geolocation of the VPN server you selected as your real location. And the encrypted data will not fall into the hands of advertisers, hackers and security services.
Types of VPN protocols
VPN security protocols are tools that encrypt data in a VPN tunnel and allow you to maintain user privacy in the open Internet. At the moment, the vast majority of modern VPN services use one of the following three VPN protocols:
IPSec. One of its main advantages is that it is available on most devices and operating systems and provides a high level of security. However, the use of double encapsulation in this protocol may result in a lower connection speed.
OpenVPN. This modern protocol is open source, so third-party manufacturers can improve and update the technology.
WireGuard. Its main advantages are ease of use, high efficiency and low vulnerability to attacks.
In addition to these VPN protocols, there are others (for example, TLS, SSTP, IKEv2), but they are unpopular or do not meet modern data encryption standards.
AdGuard VPN also has its own protocol. One of its advantages is that the traffic transmitted using the AdGuard VPN protocol is difficult to distinguish from the regular traffic. The VPN tunnel looks like normal HTTPS traffic, making it extremely difficult to detect and block. In addition, it is based on the mechanisms of the modern HTTP/2 protocol, which ensures high connection speed.
VPN drawbacks
Despite the obvious advantages, VPN is not perfect and has some disadvantages:
Lower speed
Since your traffic does not go directly to the web server, but first passes through the VPN server, the speed of the VPN connection decreases. Other factors also affect the speed when using a VPN: the load of the VPN server, its bandwidth, the compatibility of the VPN protocol with your operating system. All these factors, as well as the speed of the network itself, may impact the overall user experience of a VPN connection.
Access blocking
Some online services make a lot of effort to detect VPN traffic and block access to VPN users. However, not many VPNs can mask themselves in such a way that they are only seen as regular traffic. Therefore, many attempts to reach a certain website via a VPN connection end in nothing.
VPN connections breaking
A weak signal, network overload, VPN incompatibility with a firewall, antivirus and other programs, an outdated VPN protocol — all this can cause a sudden failure in the VPN connection, especially with unreliable VPN providers.
AdGuard VPN
Our VPN service has several important advantages:
Proprietary VPN protocol, which works stably even with a slow Internet connection and disguises itself as normal traffic, making it more difficult to track and block it
No-logging policy, which means no personal data can be shared with third parties because AdGuard VPN never collects such data
More than 50 VPN servers in dozens of countries
Ease of use and extensive customization options
Currently, AdGuard VPN is available as:
Browser extension for Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Opera
Command-line interface for Linux, Mac, and some routers
A VPN client for routers